General requirements to the game
To avoid unwanted firewall initiation, ARVI platform creates firewall rules for the following port range during its installation: 1770, 7777-7780. We advise developers to choose a network port for this game from this specific range.
Please also note that ARVI platform uses a number of ports for its own purposes, and the game should not be using them. The following ports should not be used: 3580, 3581, 3585, 3587, 5586, 11000-11020, 11022, 22022.
SDK installation and setup
This Integration SDK requires Unity 2017.4 or newer. Go to DOWNLOADS section and download unity package. In Unity select Assets 🡒 Import Package 🡒 Custom Package. Select the SDK package file and import it into Unity.
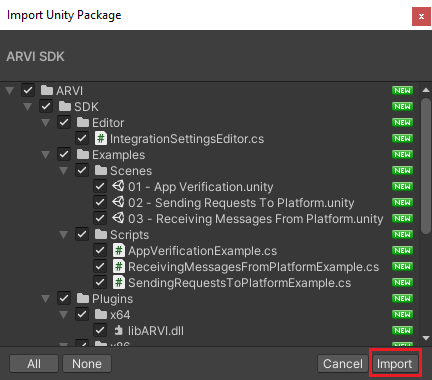
Note: When you install new SDK versions, close Unity, delete the ARVI\SDK folder, and repeat the installation process.
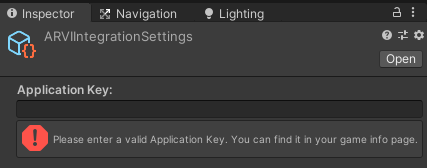
After SDK is imported into Unity, a new ARVI menu will appear. Select ARVI 🡒 Integration 🡒 Settings. Please specify the Game Key in the Application Key field. You can get this key in the game info section of your developer account on our website.
Platform integration
All features required for integration are in the Integration class. A detailed description of its methods follows. The folder ARVI/SDK/Examples contains the most common integration usage examples.
Properties
Property | Description |
|---|---|
AppKey | Application Key, provided with API and used for entitlement checks |
Initialized | Gets if the integration API initialized and ready to use. If API is not initialized, you should call Initialize method |
PlayerDominantHand | Player’s dominant hand. Useful for games where it is important to know if the player is right-handed or left-handed |
PlayerID | Session-unique player ID. Can be useful for identifying a player in a session |
PlayerName | Player name. Initially can be set by the operator in the admin panel before starting the game, but can be empty if the name is not set. You can set it yourself using the SetPlayerName method if your game supports player name input. If you set this property yourself, the specified name will be displayed in the operator’s admin panel |
PlayersCount | Number of players for whom a game was launched |
ServerIP | Game server IP address |
SessionID | Unique game session identifier. Can be useful for separating sessions if there are several sessions of your game running on the network and you are looking for players on the network yourself |
SessionLanguage | Game language selected by the operator in the admin panel before launch. Presented as a two-letter abbreviation (ISO 639-1). EN, DE, FR, etc. |
SessionTime | Game session time in seconds. Typically, this is the value you set in the Game timeout field of the game manifest |
ShouldApplicationTrackCordTwisting | Indicates to the game whether it should track cord twisting. By default it is set to True. False value is set for wireless headsets |
Methods
Method | Description |
|---|---|
IsApplicationEntitled | Checks if application is entitled to run on this computer |
ServerStarted | Sends a notification to the platform about the launch of the game server. You should call this method when your game server is ready to accept connections |
GameCompleted | Sends a notification to the platform about the end of the game. Call this method when the game is over |
CallOperator | Sends a request for operator assistance to the platform. Bind a call to this method to game objects in the game so that players can request operator assistance |
SetAudioChatChannel | Sets an audio chat channel. Useful for games where there is a division into teams so that players on one team do not hear the players on the other |
ActivateInGameCommand | Activates in-game command. If several commands have the same activation message, then they will all be activated |
ActivateInGameCommands | Activates multiple in-game commands at once |
DeactivateInGameCommand | Deactivates in-game command. If several commands have the same deactivation message, then they will all be deactivated |
DeactivateInGameCommands | Deactivates multiple in-game commands at once |
SendLogMessage | Sends text message to platform log |
SendTrackingMessage | Sends tracking message. It will be used for your events visualization |
SetPlayerName | Sets the new player name. Use this method if your game supports player name input |
SetPlayerDominantHand | Sets the new player dominant hand. Use this method if your game supports player dominant hand selection |
SetSessionData | Sets session-related data by name. You can create your own custom local (not network) variables that will be stored in the platform during the entire session. It can be useful if your game restarts within the same game session to load previously saved settings |
TryGetSessionData | Gets session-related data saved with SetSessionData method |
TryGetUISettings | Gets UI settings by name. For more information about how the UI settings work, see the UI Settings section |
Events
Event | Description |
|---|---|
PlatformMessageReceived | Fires when the platform sends message to the game. Use to handle in-game commands |
TimeLeftRequest | Fires when the platform asks the game for time until the end of the session. See Time Left Request handling for details |
PlayerPositionRequest | Fires when the platform asks the game for the 3D coordinates of the player in the world. See Player Position Request handling for details |
PlayerNameChanged | Fires when a player’s name has been changed by the operator in the admin panel. Use to update the player’s name in the game |
PlayerDominantHandChanged | Fires when a player’s dominant hand has been changed by the operator in the admin panel. Use to update the player’s dominant hand in the game |
Initialization and verification
The first step is to initialize SDK on your integration module by calling the Integration.Initialize() method.
using ARVI.SDK;
...
protected virtual void Awake()
{
// Initialize integration API
if (Integration.Initialize())
Debug.Log($"ARVI SDK {Integration.Version} initialized");
}
To make sure that the game is launched on the computer with the running ARVI platform and is authorized for launch at the current game location, the verification process should be executed as soon as possible. Verification is launched using the Integration.IsApplicationEntitled() method and does not require Internet connection.
using ARVI.SDK;
...
protected virtual void Start()
{
// Verify application. You can handle result in OnComplete callback
Integration.IsApplicationEntitled().OnComplete(EntitlementCheckCallback);
}
protected virtual void EntitlementCheckCallback(Response response)
{
if (response.Success)
{
Debug.Log("Entitlement check passed");
}
else
{
Debug.LogWarning($"Entitlement check failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
UnityEngine.Application.Quit();
}
}
When the verification is completed, the handler will receive the check results. If the check fails, game must shut down.
Platform request handling
From time to time, the platform may be sending requests for certain information. There are several types of requests that may be sent by the platform:
- Time Left Request. If the game has any time limitations, it will respond with the number of seconds left until the game is over. This information will appear in the platform control panel.
- Player Position Request. Our platform features 3D audio chat, and accurate voice positioning requires physical location of the player in the game world. The game will respond to this request by sending the player’s coordinates in the game and the player’s Forward and Up vectors.
Note: The frequency of the Player Position Request is approximately 10 times per second.
Handling these requests requires subscribing to them and specifying the relevant handlers.
using ARVI.SDK;
...
protected virtual void OnEnable()
{
// Subscribe to requests for remaining time
Integration.TimeLeftRequest += HandleTimeLeftRequest;
// Subscribe to requests for player position in game
Integration.PlayerPositionRequest += HandlePlayerPositionRequest;
}
protected virtual void OnDisable()
{
// Unsubscribe from requests for remaining time
Integration.TimeLeftRequest -= HandleTimeLeftRequest;
// Unsubscribe from requests for player position in game
Integration.PlayerPositionRequest -= HandlePlayerPositionRequest;
}
protected virtual void HandleTimeLeftRequest(out int seconds)
{
// You need to return a value showing how many seconds are left until the end of the game
seconds = 3600;
}
protected void HandlePlayerPositionRequest(out Vector3 playerPosition, out Vector3 playerForward, out Vector3 playerUp)
{
// You need to return the player's position in the game, as well as his up and forward vectors
playerPosition = transform.position;
playerForward = transform.forward;
playerUp = transform.up;
}
Handling of game commands
In addition to the above-mentioned standard requests, the platform may send in-game commands that you can create in the developer account on our website. They will be sent into the game from our control panel by the operator.
For example, you created a Skip Puzzle command with /skip command URL, +5 min command with /timemodify?minutes=5 command URL and -5 min command with /timemodify?minutes=-5 command URL. In order for your game to handle these commands, you need to subscribe to messages from the platform and specify the handler that will execute your in-game commands. Then you can handle them like this:
using ARVI.SDK;
...
protected virtual void OnEnable()
{
// Subscribe to messages from the platform
Integration.PlatformMessageReceived += HandleMessageFromPlatform;
}
protected virtual void OnDisable()
{
// Unsubscribe from messages from platform
Integration.PlatformMessageReceived -= HandleMessageFromPlatform;
}
protected virtual void HandleMessageFromPlatform(PlatformMessage message)
{
var messageName = message.Name.ToLowerInvariant();
switch (messageName)
{
// Command URL that you defined for "Skip Puzzle" command
case "skip":
// Handle your "Skip Puzzle" command here
message.SetResponse("OK");
break;
// Command URL that you defined for time modification commands
case "timemodify":
// Get the minutes value from command params
var minutes = message.Params["minutes"];
switch (minutes)
{
case "+5":
// Handle your "+5 min" command here
break;
case "-5":
// Handle your "-5 min" command here
break;
}
message.SetResponse("OK");
break;
}
}
You can also set a response for a successfully handled message using message.SetResponse, or get notified about a handling error using message.SetError.
Sending messages to the platform
Game server start message
To ensure correct operation of the platform, the computer acting as the game server must report that the game server has started. Use Integration.ServerStarted() to send this message. A single-player game must send this message immediately upon startup.
// Notify the platform about the game server launch
Integration.ServerStarted().OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("ServerStarted completed.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"ServerStarted failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
Game completed notification
The game must also notify the platform of its completion. Use the Integration.GameCompleted() method for this. We recommend call it just before closing the game, and close the game in its OnComplete handler.
// Notify the platform when the game is completed
Integration.GameCompleted().OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("GameCompleted completed.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"GameCompleted failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
CloseGame();
});
Operator call
Sometimes a player may require the operator’s assistance. You can call the Integration.CallOperator() method, which will trigger a message on the operator’s control panel indicating that the player needs help.
// Notify the platform about the need for the operator's assistance
Integration.CallOperator().OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("CallOperator completed.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"CallOperator failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
Audio chat channel selection
By default, all players in the game are on a common audio chat and can hear one another. However, multi-player games that support multiple teams might require team-based separation of audio streams. For example, players in the same team have to hear one another only and not any other teams. For this purpose, the game may ask the platform to assign a relevant audio chat channel to the user that will correspond to the player’s team number. This can be done using the Integration.SetAudioChatChannel(channel) method, where channel is the channel number. Channels 1…10 and Public are supported.
// Ask the platform to set the audio chat channel
Integration.SetAudioChatChannel(AudioChatChannel.Public).OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("SetAudioChatChannel completed.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"SetAudioChatChannel failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
Activating and deactivating in-game commands
You can control the display of in-game commands in the admin panel at a specific point in time. For example, the game provides an in-game command to restart the level, but you want to display it in the operator panel only after the level has started. Or maybe you want to hide the puzzle solving command when it has already been solved. Use Integration.ActivateInGameCommand(activationMessage) and Integration.DeactivateInGameCommand(deactivationMessage) methods for these purposes. activationMessage and deactivationMessage are messages for activating and deactivating a specific command or several commands. For more information on activating and deactivating commands, see the Developer’s Guide.
// Activate "Restart" in-game command
Integration.ActivateInGameCommand("COMMAND_RESTART_ACTIVATE").OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("Restart activated.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"Restart activation failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
// Deactivate "Skip Puzzle 3" in-game command
Integration.DeactivateInGameCommand("COMMAND_SKIP_PUZZLE3_DEACTIVATE").OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("Skip Puzzle 3 deactivated.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"Skip Puzzle 3 deactivation failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
Here the commands “Restart” and “Skip Puzzle 3” are used for example only. Your game will have its own in-game commands.
You can also activate/deactivate multiple in-game commands at once:
// Activate "Command1" and "Command2" in-game command
Integration.ActivateInGameCommands(new string[] { "COMMAND_1_ACTIVATE", "COMMAND_2_ACTIVATE" }).OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("Activated.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"Activation failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
Sending messages
If you need to report any event in the game (such as a puzzle solved), you can send a text message to the platform. It will be saved in game logs and will be available for display in the game session information on the website. Use the Integration.SendGameMessage(message, messageGroup) method to forward your message. As an optional second parameter, you can specify the group (designated using any word of your choosing), and all messages referencing this group will be grouped when displayed. Examples:
// Send some text message to platform
Integration.SendGameMessage("Puzzle 1 solved").OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("Message send.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"Message failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
// Send grouped text message to platform. It will be grouped in group Level1
Integration.SendGameMessage("Message about Level1", "Level1").OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("Message send.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"Message failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
You can also send a message that will set the timescale to a specific color when it is displayed on it. For example, you want to see (as a color on the timescale) how long it took the player to complete a certain action. Call the Integration.SendTrackingMessage(message) method and specify the relevant marker as the message.
// Send tracking message to platform. It will be used for your events visualization
Integration.SendTrackingMessage("Some Tracking Event").OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("Tracking message send.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"Tracking message failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
Sometimes, you might need to send a technical message without cluttering the game session log. For example, you want to log an error message, or send the error code, module and method that initiated it, etc. For these purposes, we recommend using the Integration.SendLogMessage(message) method. It will save your message in a separate “technical” log only without affecting the game log. Example:
// Send log message to platform. It will be stored only in service log file
Integration.SendLogMessage("Write this string to log file").OnComplete(
(response) => {
if (response.Success)
Debug.Log("Log message send.");
else
Debug.LogWarning($"Log message failed. Error code: {response.Error.Code}. Error message: {response.Error.Message}");
});
Advanced settings
Cord twist tracking
We recommend that developers implement cord twist tracking for VR headset in their games. This avoids damage of the VR headset and prolongs its service life. However, in some cases (for example, for wireless headsets) such tracking should not be used.
Our platform sends information about whether it is necessary to activate cord twist tracking or not. Use the Integration.ShouldApplicationTrackCordTwisting property at any time to determine if the game should activate cord twist tracking.
Trial Mode
When starting the game from the control panel, the operator in some cases may indicate that the game should be launched in Trial Mode. Typically, this launch mode is used for testing or demonstration purposes and is not intended for commercial use. You can use the Integration.IsApplicationInTrialMode property to understand that the game is running in trial mode and display a corresponding message in the game about it. The message can also indicate that commercial use is prohibited.
